Have you ever wished there was an easier, safer way to send or receive money—without depending on banks, online wallets, or third-party apps? That’s where blockchain technology comes in. While the word might sound technical or intimidating, its purpose is simple: to make digital transactions faster, safer, and completely transparent.
In this post, we’ll break down blockchain, cryptocurrencies, and how this revolutionary technology is transforming everything from payments to supply chains. Whether you’re new to crypto or just curious about how blockchain works, this is your beginner-friendly deep dive.
🚫 The Problem With Traditional Transactions
Imagine this scenario: four friends—Jack, Ted, Sam, and Phil—go out for dinner. Jack pays the entire bill, and the others agree to send him their share later.
The next day, Phil successfully transfers his share via online banking. But when Ted and Sam try to send theirs, their transactions fail. The reasons? Could be anything:
-
The bank is down for maintenance
-
One of their accounts is frozen
-
Daily transfer limits were exceeded
-
Or worse, unexpected transaction fees
This highlights a fundamental issue: our traditional financial systems are vulnerable to delays, errors, and middlemen.
💰 Enter Cryptocurrencies
To solve problems like these, cryptocurrencies were born. These are digital or virtual currencies that operate independently of banks, made possible through blockchain technology.
Here’s what makes cryptocurrencies unique:
-
They’re decentralized – no need for a central bank or governing authority
-
They’re secure – protected by strong cryptographic encryption
-
They’re nearly impossible to counterfeit
In a world of thousands of cryptocurrencies—like Ethereum, Litecoin, and Zcash—Bitcoin remains the most well-known and widely used.
🔗 How Blockchain Actually Works
Let’s revisit our dinner story—but this time, the friends use Bitcoin to settle their debt.
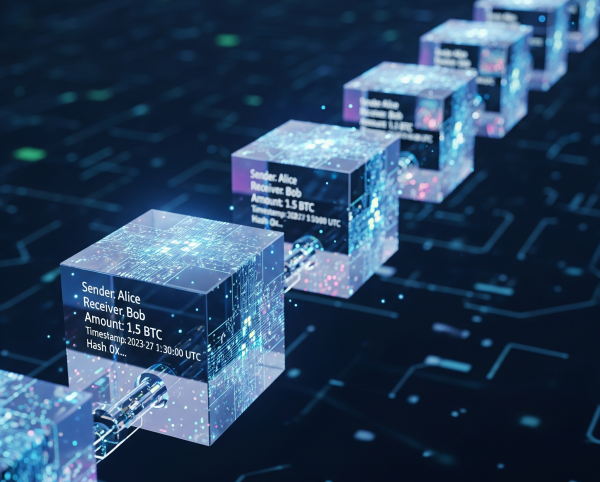
Phil, Ted, and Sam each send Jack two bitcoins. Every time a transaction happens:
-
A block is created that records all details of the transfer
-
This block also logs how many bitcoins each person now holds
After Phil sends two bitcoins, a block is created:
-
Jack now has 7 bitcoins (he had 5)
-
Phil has 1 (he had 3)
When Ted and Sam send theirs, separate blocks are created and linked together, forming a chain of blocks—aka the blockchain.
Now here’s the brilliant part:
Everyone involved has a shared copy of this transaction history. If Phil tries to send more bitcoins than he owns, the system rejects the transaction because everyone can clearly see he doesn’t have the funds. It’s fully transparent, tamper-resistant, and self-validating.
🔐 The Role of Keys: Public vs Private
Each user in a blockchain system has two keys:
-
A public key (like your email address)
-
A private key (like your password)
Let’s say Phil sends bitcoins to Jack. He enters:
-
How many bitcoins to send
-
Jack’s wallet address (public key)
-
His own wallet address (public key)
The transaction data is run through a hashing algorithm, and Phil digitally signs the transaction using his private key. This confirms he is the one initiating the payment.
Then, using Jack’s public key, the transaction is broadcasted across the blockchain network. Only Jack’s private key can unlock the incoming bitcoins—keeping it both secure and private.
Bitcoin uses the SHA-256 algorithm for encryption, while others like Ethereum use their own systems like Ethash.
⛏️ Mining and Proof of Work
Each transaction isn’t instantly added to the blockchain. It needs to be verified by users called miners.
Miners solve complex mathematical puzzles to validate each block. The first to solve it gets to add the block to the chain—and is rewarded with cryptocurrency, such as 12.5 bitcoins.
This process is called:
-
Proof of Work – solving the puzzle
-
Mining – adding the block to the blockchain
Once verified, the wallets of everyone involved are updated in real-time.
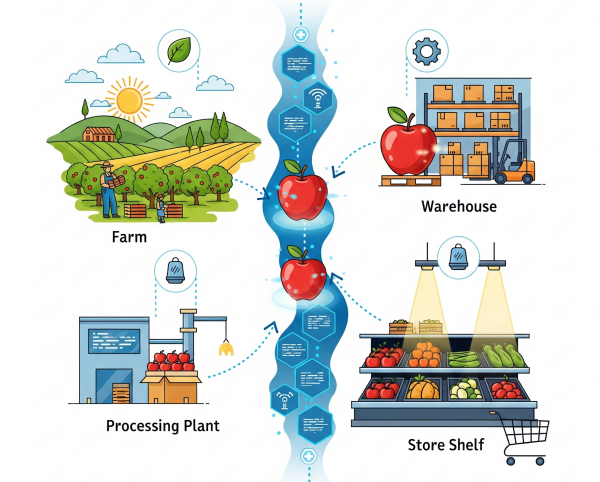
🏪 Real-World Example: How Walmart Uses Blockchain
Blockchain isn’t just for digital currencies—it’s changing how companies do business, too.
Walmart faced challenges with product quality and high return rates. When customers returned damaged items, Walmart couldn’t easily trace where things went wrong—was it during farming, transport, or storage?
So they implemented blockchain technology.
Now, each step in their supply chain is logged in blocks—from farm to shelf. If a customer returns a product, Walmart can instantly trace its journey and pinpoint where the issue occurred. This allows them to:
-
Improve accountability
-
Reduce waste
-
Enhance customer trust
And this is just one example. Blockchain is now being used in healthcare, real estate, logistics, voting systems, and more.
🧠 Final Thoughts: The Future Is Decentralized
Blockchain is more than a buzzword—it’s a paradigm shift. It changes how we think about trust, ownership, and digital transactions.
Whether you’re splitting dinner with friends or managing a global supply chain, blockchain brings transparency, security, and efficiency to the table.
And the best part? It’s just getting started.